Clene (NASDAQ:CLNN) is developing a novel approach for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease, using nanocatalysts in order to enhance cellular energy production.
“We have developed a new class of drugs using biologically active nanocrystals designed to catalyze energy-producing reactions in the body and enhance cellular repair by increasing cellular energy,” Rob Etherington, CEO, says in an interview with BioTuesdays.
“These drug candidates are clean-surfaced, metallic nanocrystals suspended in highly pure water and are taken orally, daily,” he adds.
Clene’s lead drug candidate, CNM-Au8, is a stable suspension of pure gold nanocrystals, suspended in water. It is designed to enhance critical intracellular energy-producing reactions necessary for repairing and reversing neuronal damage. “We started with gold because it has a long history of medicinal efficacy, with a unique atomic structure that lends it to catalysis at the nano scale.”
Mr. Etherington says CNM-Au8 has shown promising efficacy in improving neurological function in multiple preclinical studies and has demonstrated effects on key brain energetic metabolites in patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
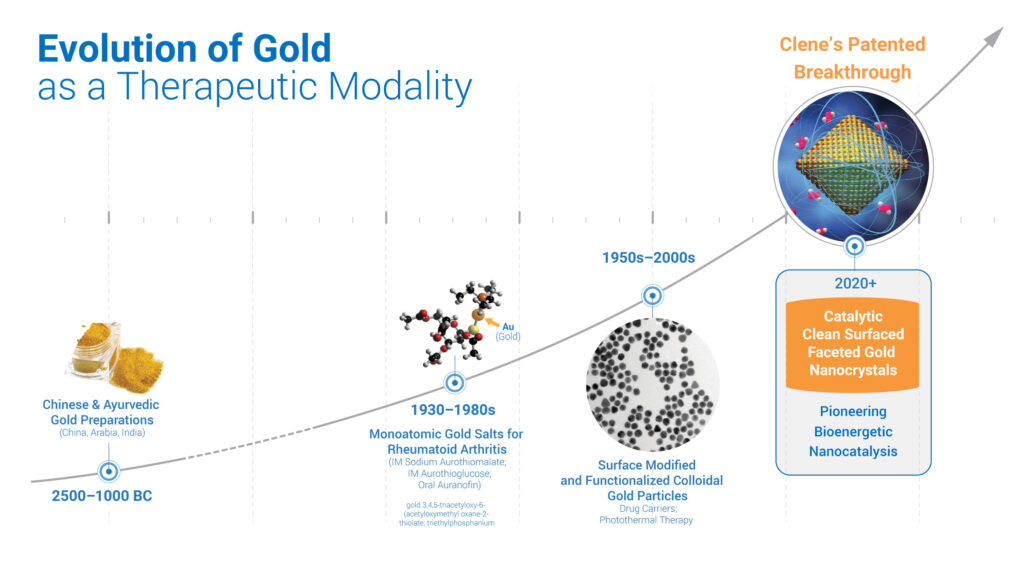
“Clene’s patented breakthrough is the production of biologically active, clean-surfaced gold nanocrystals that cross the blood-brain-barrier. These self-assembled nanocrystals, resulting from Clene’s proprietary manufacturing methods, have not exhibited toxicities historically associated with synthetic gold compounds or nanoparticles made from synthetic production methods,” he contends.
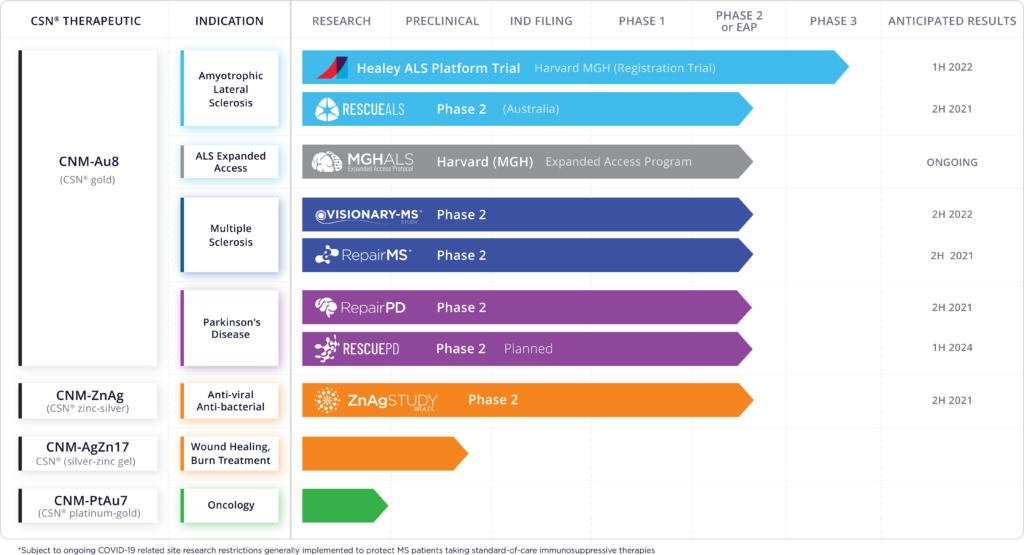
CNM-Au8 is under investigation in multiple clinical trials for disease modification in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, including a Phase 3 registration trial in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (HEALEY-ALS platform); a Phase 2 study in ALS (RESCUE-ALS); a Phase 2 study in MS (VISIONARY-MS) for the treatment of stable relapsing multiple sclerosis; and Phase 2 target engagement studies in Parkinson’s disease and MS (REPAIR-PD and REPAIR-MS).
“Over the next four-to-five quarters, we will be releasing data to show whether CNM-Au8 can improve neurological function,” Mr. Etherington says.
If successful, CNM-Au8’s global market opportunity is significant. According to studies published in Lancet Neurology and other data forecasting publications:
- Treatments for ALS are projected to exceed $1-billion annually by 2029. Mr. Etherington says the sector has had only modest success developing drugs in recent decades, with only two drugs approved for ALS, neither of which dramatically lengthens patient lifespan or improves quality of life.
- Multiple sclerosis affects some 2.5 million patients globally, representing a current market opportunity of $23-billion. The only approved treatments are immunomodulators designed to prevent an immune system attack, without improving neurological function, he adds.
- And Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disease, is expected to affect some seven million patients globally by 2025, with drug sales projected at $6-billion. Only symptomatic treatments have been developed for Parkinson’s, again with no change in neurological function, Mr. Etherington adds.
Clene’s IP is protected by more than 100 issued and 30 pending patents that protect state of matter claims, myelin protection mechanisms, remyelination and neuroprotection to 2035 as well as trade secrets. Its manufacturing and process patents extend to 2030 and beyond.
The company also has developed a silver-zinc ionic solution that is being studied in a Phase 2 trial in Brazil as an anti-viral and anti-bacterial, with data expected in the second half of 2021.
Mr. Etherington explains that existing approaches to treating neurodegenerative disorders target singular mechanistic pathways, such as attempting to reduce the amount of specific misfolded proteins or modulating specific receptors.
“Our approach is decidedly different as we try to impact the mechanisms responsible for cellular energy impairment underly the disease itself by increasing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which results in increased adenosine triphosphate, improving proteostasis, and directly decreasing reactive oxygen species.”
In preclinical studies, he says CNM-Au8 has demonstrated increased cellular energy production, resulting in neuro-repair of damaged neurons and remyelination.
Last month, Clene reported positive blinded interim efficacy data from its ongoing Phase 2 RESCUE-ALS proof-of-concept study, evaluating the efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of CNM-Au8 in the treatment of early symptomatic ALS patients.
The 36-week study enrolled 45 patients, with half receiving CNM-Au8 and half placebo.
The RESCUE-ALS study’s primary efficacy endpoint over nine months is to look at the change in Motor Unit Number Index (MUNIX), a sophisticated electromyography technique that is a sensitive predictor of clinical decline. MUNIX measures the change in the estimated number of functioning motor neurons serving four specific muscles. Key secondary endpoints include measuring pulmonary and physical function.
The interim data indicated that the enrolled cohort performed better than expected on the primary endpoint, based on an expected, continuous decline seen in published data from prior observational studies, Mr. Etherington says.
Enrollment at two sites in Australia was completed in the second half of 2020, with topline data anticipated in the second half of 2021. So far, with more than 140 patient-years of human exposure, CNM-Au8 has been shown to be well tolerated with no dose-limiting safety issues.
“While this data remains blinded, we believe these data may support CNM-Au8’s potential to become a breakthrough for this devastating disease,” Mr. Etherington suggests.
In parallel to the Phase 2 RESCUE-ALS study, he says Clene is participating in a Phase 3 clinical program with CNM-Au8 – the HEALEY ALS platform trial – as well as an expanded access program for ALS patients that were unable or too sick to enter the trial.
The 24-week HEALEY Platform Trial is an ongoing multi-drug platform trial, with 160 ALS patients enrolled in the CNM-Au8 study across three arms. Forty patients will receive placebo and 120 will receive one of two doses of CNM-Au8. The double-blind study was half enrolled in March, with topline data slated for release in the first half of 2022.
The primary endpoint is a change in the ALS Functional Rating Scale, which is a validated rating instrument for monitoring the progression of disability in patients with ALS. Secondary endpoints include measures of breathing and muscle function.
The HEALEY ALS trial is funded by philanthropic donors and led by Harvard’s Massachusetts General Hospital, with more than 50 other centers of excellence participating. HEALEY is the first-ever ALS platform trial designed to reduce trial time, costs, and increase patient participation in developing novel therapies.
To measure CNM-Au8’s effects on brain bioenergetic metabolites, Mr. Etherington says Clene is conducting two Phase 2 target engagement studies – REPAIR-PD and REPAIR-MS – in Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis patients.
Interim results from both REPAIR studies indicated encouraging improvements in brain metabolic biomarkers, including elevated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels and normalized adenosine triphosphate levels, indicating a homeostatic effect of CNM-Au8 on brain bioenergetics in patients, he adds.
Final data from REPAIR-PD and REPAIR-MS are expected in the second half of 2021. Clene plans to initiate an additional Phase 2 efficacy trial with CNM-Au8 in Parkinson’s patients by the end of 2021.
Clene also is conducting a 150-patient placebo-controlled Phase 2 VISIONARY-MS trial in Australia and North America, evaluating the efficacy and safety of CNM-Au8 as a remyelinating and neuro-reparative treatment in stable relapsing MS patients with chronic visual impairment. The study also is measuring functional improvement in walking ability, working memory and upper extremity dexterity.
Mr. Etherington says interim blinded data from the VISIONARY-MS trial demonstrated notable, exposure-related median improvements in both low contrast letter acuity, the primary endpoint, as well as the other core components of the modified MS functional composite scale. Full enrollment in the Phase 2 trial is expected by the first half of 2022.
“Our bioenergetic nanocatalyst has the advantage of clinically exploring three neurodegenerative diseases at the same time, which is a very unique thesis,” Mr. Etherington says.
• • • • •
To connect with Clene or any of the other companies featured on BioTuesdays, send us an email at [email protected].