
Hepion Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ:HEPA) reported positive topline results from its recently completed Phase 2 ALTITUDE-NASH clinical trial with lead drug candidate, rencofilstat.
ALTITUDE-NASH met its primary endpoint by demonstrating improved physiologic liver function and was well tolerated after four months of treatment in subjects with Stage 3 or greater fibrosis based on the AGILE 3+ criteria.
All additional secondary endpoints were also met, including reductions in the liver injury biomarkers, alanine and aspartate transaminases (ALT and AST), and multiple fibrosis-associated biomarkers, including ProC3 (procollagen 3 C-terminal peptide); PIIINP (procollagen 3 N-terminal peptide); TIMP1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1); hyaluronic acid; and enhanced liver fibrosis scores (composite of PIIINP, TIMP1, and hyaluronic acid).
These observations build on similar findings from a shorter Phase 2a trial and reinforce rencofilstat’s direct antifibrotic mode of action and increase the confidence for reductions in fibrosis in Hepion’s ongoing Phase 2b ASCEND-NASH paired biopsy trial.
“We are thrilled that the ALTITUDE-NASH trial met both its primary efficacy and safety endpoints, in particular with the 225 mg rencofilstat dose showing the greatest benefit to liver function and multiple NASH-associated biomarkers,” Todd Hobbs, M.D., CMO of Hepion, said in a statement.
“This trial was designed to inform us on how well rencofilstat improves hepatic function in those with significant impairment and risk for complications from their advanced NASH,” he added.
Dr. Hobbs said ALTITUDE-NASH also provided an opportunity to evaluate data generated from different doses of rencofilstat. “Our improved understanding of which subjects best respond to rencofilstat can be immediately applied to increase the likelihood of success of our larger and longer ASCEND-NASH paired biopsy trial.”
In the primary endpoint, four measures of liver impairment significantly improved, compared with baseline, with four month of rencofilstat 225 mg treatment.
The HepQuant SHUNT test was used in this study under an FDA-issued investigational device exemption. The SHUNT test is a minimally invasive test that tracks changes in the degree of liver function impairment and was used to determine four key measures: HepQuant DSI (disease severity index) score, which primarily reflects hepatocyte function; SHUNT, which reflects the impact of micro-architectural changes, such as fibrosis on blood flow through the liver; HepQuant HR (hepatic reserve); and RISK ACE, which reflects the annual risk of a patient developing an adverse clinical outcome (Table 1).
Rencofilstat met the primary endpoint and lowered mean DSI score in all doses, with rencofilstat 225 mg treatment over four months resulting in statistically significant decreases in DSI, SHUNT %, HR %, and RISK ACE, compared with baseline; and 61% of subjects in the 225 mg rencofilstat arm had a DSI improvement of greater than 2.0 points.
In HepQuant’s research, improvements from baseline, especially for high DSI scores that decrease by 2.0 points or more, are associated with clinically significant reductions in risk for liver related complications, including esophageal varices and encephalopathy.
Table 1: HepQuant Test Results in All Subjects with Paired Data (n=61)
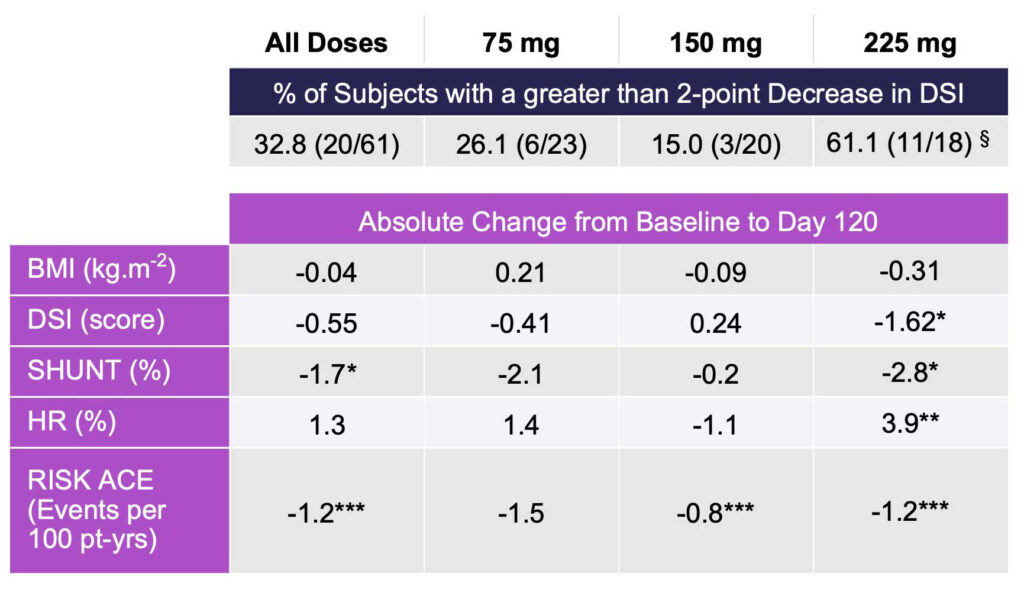
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; paired t-test, no correction for multiple comparisons
§Chi-Square p < 0.05
In subjects with the most advanced functional impairment, four measures of liver impairment significantly improved compared to baseline with rencofilstat treatment for 4 months, independent of dose.
To address the potential of rencofilstat for patients with the most advanced functional impairment and greatest risk of disease progression, an analysis was conducted on the 34 subjects with DSI greater than 17 or SHUNT % greater than 25 as research indicates these subjects are at high risk for hepatic complications (Table 2).
In this subgroup, independent of rencofilstat dose, statistically significant decreases at Day 120 compared with baseline were again observed for DSI score SHUNT %, HR %, and RISK ACE.
The large reduction in SHUNT % suggests alleviation of micro-architectural defects as anticipated from an antifibrotic agent and suggests that rencofilstat may be most effective in patients with more severe liver impairment.
Table 2: HepQuant Test Results in Functionally Impaired Subjects with Paired Data (n=34)
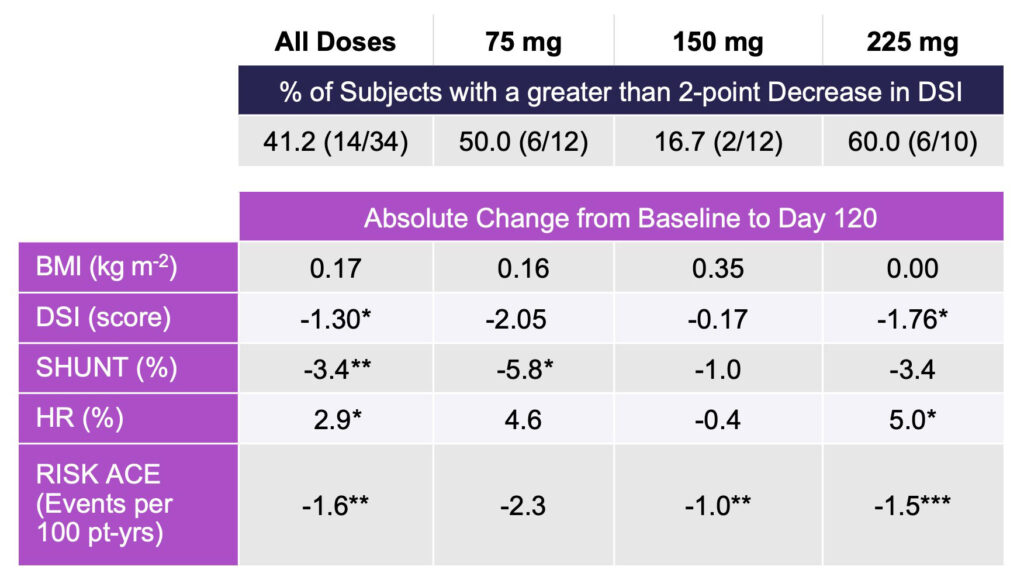
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; paired t-test, no correction for multiple comparisons
Among secondary endpoints, fibrosis and injury-associated biomarkers improved with all doses of rencofilstat, with the greatest reductions observed with the 225 mg arm.
Multiple biomarkers related to fibrosis were improved following four months of treatment with rencofilstat: ProC3, PIIINP, TIMP1, and hyaluronic acid. ELF scores were similarly improved by rencofilstat. Robust reductions in ALT and AST were also observed with all doses of rencofilstat, with the greatest reductions seen in the 225 mg rencofilstat dosing arm. Incremental dose-response patterns were observed for most of the biomarkers, and in all cases the largest reductions from baseline for each of the biomarkers occurred in the 225 mg rencofilstat group (Table 3).
Table 3: Percent Change from Baseline in Key NASH Biomarkers After Four Months Treatment with Rencofilstat
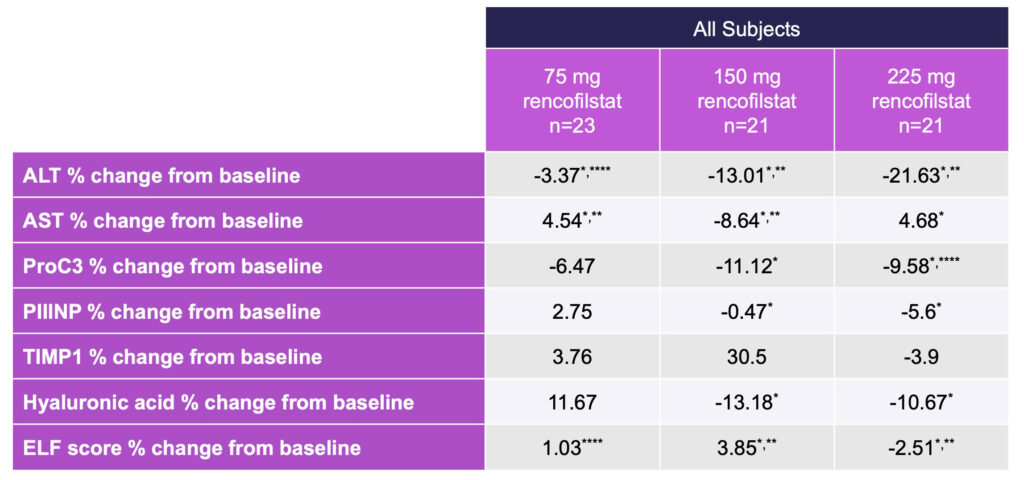
*Different from Baseline p < 0.001, Friedman ANOVA, **Different from 75 mg Dose p< 0.01,
***Different from 150 mg Dose, ****All Doses p < 0.001.
Rencofilstat 225 mg in high-risk population led to the greatest improvements in NASH biomarkers.
Additional analyses were performed on the approximate one-third of subjects with elevated baseline ProC3, which assesses the formation of Type III collagen and indicates both severity and activity of disease.
Because Pro-C3 is a measure of collagen cleavage during active fibrinogenesis, subjects with high ProC3 levels represent a NASH population with more active disease, therefore representing an important target population for many NASH drug candidates.
In ALTITUDE-NASH, the greatest magnitude of effects was observed with 225 mg rencofilstat (Table 4), and most frequent dose-dependencies were observed in subjects with baseline ProC3 greater than or equal to 37.5 ng/ml (Roche, Elecsys).
Rencofilstat 225 mg, and often the 150 mg dose, led to greater improvements than with 75 mg rencofilstat for all the NASH biomarkers in this high-risk population as well as in the entire study population.
Table 4: Percent Change From Baseline in NASH Biomarkers in Subjects with ProC3 ≥ 37.5 ng/ml
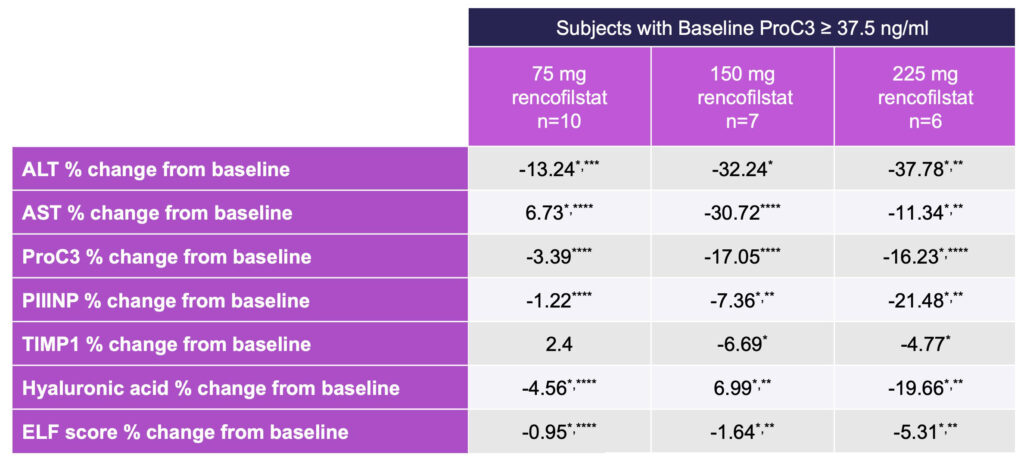
*Different from Baseline p < 0.001, Friedman ANOVA, **Different from 75 mg Dose p< 0.01,
***Different from 150 mg Dose, ****All Doses p < 0.001.
Hepion said primary safety and tolerability endpoints were met with no serious adverse events attributed to rencofilstat.
Of the 70 subjects enrolled in the study, 67 completed all study procedures, including 120 days oral dosing of rencofilstat with a 14-day routine safety follow up period.
ALTITUDE-NASH was designed as a Phase 2, multi-center, randomized, open label study. Subjects were randomized to one of three rencofilstat treatment groups, receiving either 75 mg, 150 mg, or 225 mg soft gelatin capsules once daily for a period of four months. The trial also serves as a bridge to Hepion’s current 12-month Phase 2b ASCEND-NASH liver biopsy-based trial.
Gregory Everson, M.D., founder and CEO of HepQuant, said the results from HepQuant’s testing platform provide compelling evidence that those patients at the highest risk of complications are the ones that responded most consistently and robustly to treatment with rencofilstat.
Stephen Harrison, M.D., chairman and co-founder of Summit Clinical Research and chairman of Hepion’s scientific advisory board, said improvements in numerous NASH biomarkers in concert across this population not only affirms the positive results in this four-month study but also increases confidence in positive outcomes in the larger and longer Phase 2b ASCEND-NASH biopsy trial which is currently recruiting well.
Patrick Mayo, Ph.D., Hepion’s SVP of clinical pharmacology and analytics, said ALTITUDE-NASH represents a “veritable data bonanza,” providing Hepion with information on patient responsiveness to rencofilstat in a very advanced NASH population that will further enhance the AI-POWR platform, which should allow predicting rencofilstat-responders a priori.
“This not only enhances and de-risks future studies, including potential Phase 3 trials, but will ultimately allow clinicians to provide rencofilstat to patients who they know will respond. Determining which patient is best suited to receive rencofilstat could ultimately provide guidance to our eventual commercial strategy,” he added.






