Mauna Kea Technologies (Euronext Growth:ALMKT), inventor of the world’s first and only real-time in vivo cellular imaging platform, Cellvizio, designed to deliver high-magnification visualization of cellular structures and functions, is launching CellTolerance, a unique program for the detection and treatment of food intolerances associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
“We are integrating our breakthrough cellular imaging technology, Cellvizio, with practical clinical applications to potentially change how millions of patients across North America and Europe manage their food-related IBS and overall health,” Sacha Loiseau, Ph.D., founder, chairman, and CEO of Mauna Kea Technologies, says in an interview with BioTuesdays.

“More than one in ten individuals throughout the U.S. and Europe struggle with IBS symptoms, and more than half of these sufferers endure the challenges of atypical food allergies that are difficult to identify and treat,” he adds.
IBS is a condition affecting the gastrointestinal tract and can have a range of causes or triggers. Quality of life for patients living with IBS can be significantly reduced as the disorder causes abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea and/or constipation.
“Current diagnostic methods for food intolerances can be invasive, inefficient, and often uncertain, resulting in missed diagnoses and poor patient outcomes,” Dr. Loiseau says. “We intend to transform how physicians diagnose and treat food intolerances with our CellTolerance program using Cellvizio technology, building on insights from clinicians and IBS patients.”

Dr. Loiseau explains that the award-winning Cellvizio real-time in vivo imaging platform uses confocal laser endomicroscopy to provide physicians with cellular visualization virtually anywhere in the human body. Confocal miniprobes are inserted into the existing working channel of standard endoscopes or needles, enabling physicians to monitor the progression of disease over time, assess real-time reactions as they happen, classify indeterminate areas of concern, and guide surgical interventions.
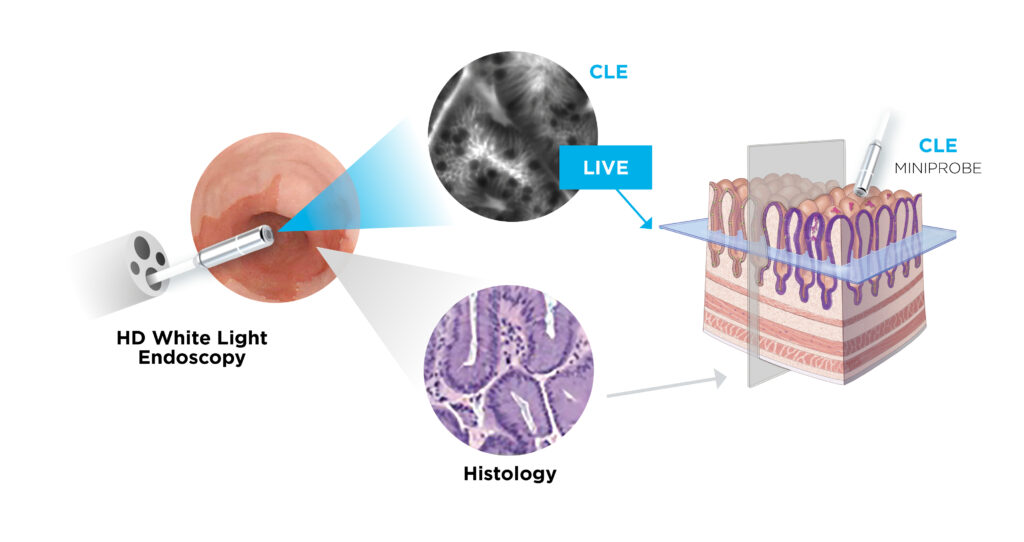
Cellvizio technology is currently used globally across a wide-range of medical specialities, including gastroenterology, pulmonology, urology, and surgery. It promotes early cancer detection, assists physicians in making better-informed decisions, and enables the potential for personalized medicine.
“Over the past fifteen years, Cellvizio technology has been the subject of more than 1100 peer-reviewed publications and is utilized in hundreds of medical institutions around the world,” Dr. Loiseau highlights.
At one such medical institution in Germany, a group of physicians surmised that endomicroscopy technology could be used to determine an IBS patient’s reaction to specific food, Dr. Loiseau recalls. In a prospective study published in the top-tier, peer-reviewed journal Gastroenterology, involving 155 IBS patients, physicians sprayed pure food on the intestinal barrier via endoscope and visualized it using confocal laser endomicroscopy. The study concluded that more than 50% of the IBS patients had a reaction clearly linked to a specific food intolerance.
“Traditional diagnostic methods had failed to detect the cause of these patients’ symptoms, underscoring the critical need for innovative solutions in this patient population,” he adds.
The CellTolerance program, using Cellvizio technology, provides physicians direct visualization of food-induced barrier impairment, enabling them to make accurate diagnoses. “This has never been done before,” Dr. Loiseau contends.
Moreover, new data presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024 in Washington, DC, demonstrated that patients who underwent a CellTolerance-guided food elimination diet saw a significant reduction in their IBS symptom severity score compared to the pre-test baseline.
“Most notably, patients experienced a worsening of symptoms when that particular food was reintroduced. The CellTolerance approach was proven to reduce symptoms in 96% of patients,” Dr. Loiseau says.
Mauna Kea’s science-based CellTolerance program, developed in collaboration with physicians and dieticians, is a viable screening tool for patients who have tested negative for food allergies or celiac disease but continue to have unresolved symptoms, he adds.
CellTolerance employs a multi-disciplinary approach to detect and treat food tolerances in IBS. In addition to live cell response visualization via the intestinal barrier’s microscopic response to select foods using Cellvizio technology, the CellTolerance program includes personalized dietary monitoring and supervised elimination diets.
Along with an accurate diagnosis, the comprehensive program will offer patients consultations with dieticians, gastroenterologists, and psychologists, as needed, to aid in achieving fast, personalized, sustainable results.
The company is also focused on pediatric applications of CellTolerance, addressing undetected food intolerances in children, which, if left undiagnosed and untreated, can have major negative effects on a child’s growth and dramatic consequences on organ function, Dr. Loiseau says. “Encouraging results have already been presented in pediatrics, and we expect some very exciting results from more recent studies to be presented soon.”
In a large-scale market research study on the IBS patient experience, including diagnosis, treatments, and diets, Mauna Kea found that 37% of the over 550 respondents believe current tests and elimination diets fail to provide definitive answers or clear treatment pathways. Additionally, 64% reported suffering for ten years or more, 33% described their symptoms as out of control, 20% said they actively seek medical help every three months, and 40% are seeing a physician once or twice a year for IBS-related issues.
“Approximately 40 million patients in the U.S. alone suffer from IBS, undergoing numerous tests, including colonoscopies, endoscopies, stool, blood, and imaging tests, and elimination diets to no avail. This is not only a burden to the healthcare system but it is very traumatic for the patient, causing enormous stress and anxiety,” Dr. Loiseau points out.
Based on strong clinical science and real-world evidence, the company decided to best develop the CellTolerance program in a new wholly owned subsidiary that is being incorporated, with the Cellvizio technology platform as a key component. CellTolerance aims to form strategic partnerships with clinic networks worldwide, focusing on ensuring continuous training and ongoing support for healthcare professionals to optimize the technology.
The company intends to launch CellTolerance at scale in key markets, including the U.S., France, Germany, Italy, and Switzerland, with the addressable market in these countries representing an opportunity estimated at $1.5 billion.
CellTolerance also aims to provide patients, providers, and partners with innovative digital tools, such as apps, to monitor symptoms and collect real-world and clinical data to be leveraged in developing advanced AI models, Dr. Loiseau suggests. “Clinical insights garnered from the CellTolerance program could empower pharmaceutical and nutrition companies to develop personalized treatments, optimize nutritional plans, and predict individual responses to therapies and dietary interventions.”
• • • • •
To connect with Mauna Kea Technologies or any other companies featured on BioTuesdays, send us an email at editor@biotuesdays.com.